In today’s world, sustainability has become an increasingly critical issue. With the growing concerns about environmental degradation, the need for eco-friendly alternatives in various industries is more pressing than ever. One such material under scrutiny for its environmental impact is Plombon. But what exactly is Plombon, and is it sustainable?
This article will take you through the key aspects of Plombon, how it is used, and its environmental effects. We will also explore whether this material can be deemed environmentally friendly or if there are alternative materials that could replace it in the future.
What is Plombon?
Plombon is a synthetic material commonly used in various industrial applications, including manufacturing, construction, and technology. Its unique properties make it a go-to material in many products, but its production and disposal processes raise some concerns. Understanding its environmental impact requires analyzing its lifecycle—from production to disposal—and how its sustainability compares to other materials.
The Manufacturing Process of Plombon
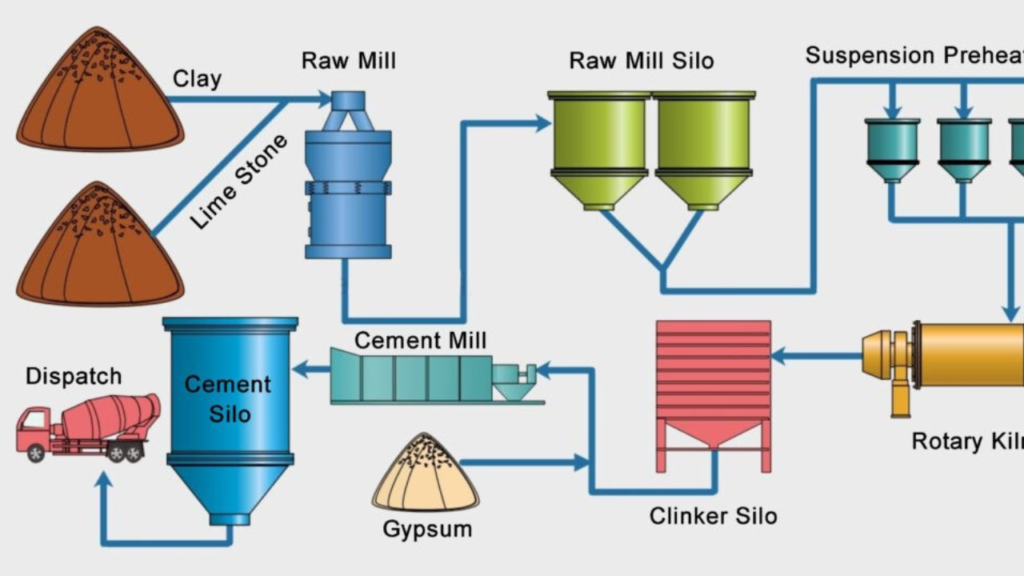
The production of Plombon involves multiple chemical processes that can have significant environmental consequences. Like many synthetic materials, it is derived from fossil fuels, contributing to air pollution and the depletion of non-renewable resources. The production process requires energy-intensive machinery and industrial practices that result in the emission of greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming and environmental pollution.
Additionally, extracting raw materials necessary for Plombon’s creation often involves mining and drilling activities that can harm local ecosystems. Deforestation, habitat destruction, and water contamination are common consequences of mining operations.
The Environmental Impact of Plombon: Pollution and Waste
Once Plombon has been manufactured and used in a product, its environmental footprint doesn’t end there. Disposal of products made from Plombon is another primary concern. Since it is not biodegradable, it can persist in landfills for centuries, leaching toxic chemicals into the soil and groundwater. The chemical components in Plombon can contaminate the surrounding environment, affecting local wildlife and the quality of water sources.
Plombon’s non-biodegradability also means it can accumulate in the environment over time, posing long-term risks to ecosystems. This accumulation contributes to the growing problem of waste in landfills and oceans. The plastic nature of Plombon adds to the broader issue of plastic pollution that is harming wildlife and natural habitats globally.
Can Plombon Be Recycled?
One key factor determining a material’s sustainability is its ability to be recycled. In theory, Plombon could be recyclable, but in practice, the recycling processes for Plombon-based products are often inefficient and underdeveloped. Many products made from Plombon are discarded in landfills, with little or no attempt to recycle them. Recycling technology has yet to catch up with the increasing use of synthetic materials like Plombon, making the recycling process expensive and time-consuming.
While some initiatives are in place to recycle Plombon, it is not yet a widespread practice. The lack of a standardized and accessible recycling system means that a significant portion of Plombon waste is in landfills, contributing to pollution.
Alternatives to Plombon: Are There More Sustainable Materials?
Given the environmental challenges associated with Plombon, it is essential to consider alternative materials that could replace it in the future. Some of these alternatives are being developed to offer similar benefits while being more environmentally friendly.
- Bioplastics: Bioplastics, made from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, provide a more sustainable alternative to synthetic plastics like Plombon. Bioplastics are biodegradable and compostable, which reduces their environmental impact. However, they still require energy for production, and there is concern over their agricultural resource consumption.
- Recycled Plastics: Recycled plastics, particularly those derived from post-consumer waste, can replace Plombon in some applications. This reduces the demand for virgin materials and helps divert plastic waste from landfills.
- Natural Materials: In some industries, natural materials such as wood, bamboo, and hemp can be used as alternatives to synthetic materials like Plombon. When sourced responsibly, these materials are biodegradable, renewable, and have lower environmental impacts.
- Eco-friendly Composites: Advances in composite materials made from natural fibers and resins offer a promising alternative. These materials are strong, durable, and lightweight, similar to Plombon, but have a significantly lower environmental impact in production and disposal.
Is Plombon Sustainable?
While Plombon offers significant functional benefits across industries, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The material’s production, disposal, and recycling challenges raise important questions about its long-term sustainability. If the demand for Plombon continues to grow, it could exacerbate environmental pollution and waste problems.
However, its impact can be mitigated by developing better recycling systems, promoting alternative sustainable materials, and adopting eco-friendly production practices. Innovations in the industry may eventually lead to a more sustainable version of Plombon, but it is not a fully sustainable option in its current form.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of Plombon is a complex issue, with concerns surrounding its production, use, and disposal. While Plombon provides essential functions across many sectors, it has its drawbacks in terms of sustainability. As industries strive for greener alternatives, it is crucial to continue exploring options like bioplastics, recycled plastics, and natural materials to reduce the overall ecological footprint of materials like Plombon.
Greater investment in recycling technologies and sustainable alternatives will be key to reducing Plombon’s environmental impact moving forward. Only time will tell whether Plombon can evolve into a more sustainable material or if we must look to alternatives to meet the challenges of a greener future.
FAQs
1. What is Plombon made from?
Plombon is a synthetic material typically made from a combination of chemicals derived from fossil fuels. Its production process requires energy-intensive machinery and industrial practices.
2. Why is Plombon considered environmentally harmful?
Plombon’s production, use, and disposal contribute to environmental pollution. Its manufacturing emits greenhouse gases, while its non-biodegradability leads to long-lasting waste in landfills, posing ecosystem risks.
3. Can Plombon be recycled?
While Plombon is technically recyclable, the current recycling systems for this material are inefficient and underdeveloped. As a result, Plombon-based products are often discarded in landfills instead of recycled.
4. What are some sustainable alternatives to Plombon?
Sustainable alternatives to Plombon include bioplastics, recycled plastics, natural materials like bamboo and hemp, and eco-friendly composites from natural fibers.
5. Is Plombon a completely unsustainable material?
Although Plombon is not entirely sustainable in its current form, improvements in recycling technologies and developing more sustainable materials may reduce its environmental impact.
You May Also Read: https://ventsbuzz.pro/cedar-ridge-apartments/




